U.S. Battery Storage Capacity to Reach 30 Gigawatts by 2025
By Anjali Joshi
According to the latest report by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Information Administration (EIA), U.S. battery storage capacity is expected to triple in the coming three years, driven by an increase in the number of hybrid projects, especially solar and storage. An EIA inventory of active projects shows that as of October 2022, utility-scale battery storage capacity stood at 7.8 GW in the United States. Developers and power plant owners have plans to increase utility-scale battery storage to 30 GW by the end of 2025, including adding 1.4 GW of battery storage capacity in the final three months of 2022.
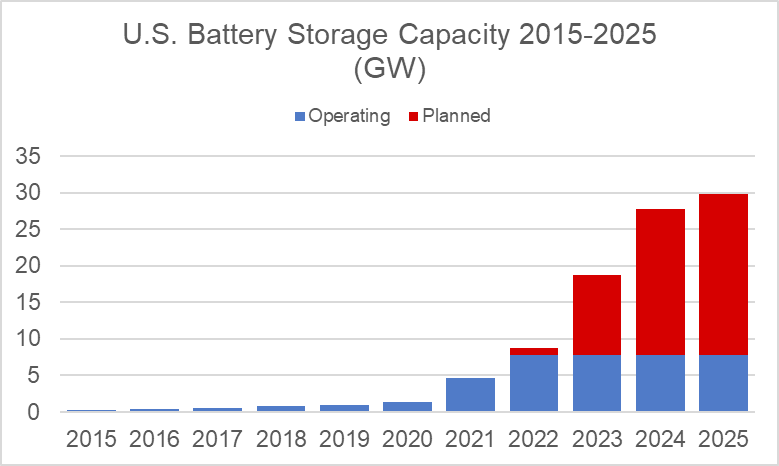
Battery storage capacity was negligible prior to 2020 but picked up the pace in the United States in 2020. EIA expects total capacity to reach 9.1 GW by the end of 2022, then double to 19 GW in 2023 and hit 28.4 GW in 2024.
The growth rate of U.S. battery storage capacity is expected to outpace the historical rate of solar capacity growth. While U.S. utility-scale solar capacity increased from less than 1 GW in 2010 to just 13.7 GW in 2015, utility-scale battery storage capacity is likely to increase from 1.5 GW in 2020 to 30 GW in 2025.
As more and more intermittent sources of energy like wind and solar are being put online, battery storage is becoming a necessity to store extra energy for later use and add stability to the grid.
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has provided additional incentives to spur deployment of battery energy storage projects, including allowing the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) to be applied to standalone energy storage and extending the 30% ITC through 2032. CEA expects both of these changes to help to drive the development of 30 GW of storage capacity by 2030.
Despite California accounting for the most utility-scale solar capacity, Texas holds the highest share of the utility-scale battery capacity which is slated to come online between 2022 and 2025. While developers plan to add 7.7 GW of solar capacity in California from 2022 to 2025, 10.5 GW of solar capacity is planned in Texas during the same period. In addition to solar, Texas currently accounts for 37.2 GW of wind power capacity, the highest in the United States. Developers plan to add another 5.3 GW of wind over the next three years, thus ramping up the need for grid-scale storage solutions in the state.
As the aggregate capacity of battery storage projects grows, so does the size of individual battery storage systems. Before 2020, the capacity of the largest battery storage project was 40 megawatts. In 2020, California’s 250-megawatt Gateway Energy Storage System marked the beginning of large-scale energy storage installations in the country. At present, the largest operating battery storage project in the United States is in Florida, the 409-megawatt Manatee Energy Storage. Developers have plans to build over 23 large-scale battery storage projects, ranging from 250 megawatt to 650 megawatt, by 2025.
Source: U.S. battery storage capacity will increase significantly by 2025 (EIA, Today in Energy)