EIA Expects Lower Natural Gas Prices
in 2023
By Christian Roselund
In a February update, U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Information Administration (EIA) has forecast that U.S. natural gas prices will fall to an average of $3.40 per Million British Thermal Units (MMBtu) over the course of 2023. This represents a 47% decrease from the average 2022 price and a 30% decrease from EIA’s forecast just a month prior, which EIA credits to a warmer than expected winter, reduced gas demand, and increased storage levels. However, it does not expect the share of electricity generation from natural gas to increase in 2023.
EIA also notes that natural gas prices remain highly volatile. Average U.S. natural gas prices were above $7/MMBtu at the Henry Hub national trading hub each month from June through September, peaking at nearly $9/MMBtu in August. This was the highest monthly price in more than a decade. Prices then fell to around $5.50/MMBtu for October through December, and then again to $3.27/MMBtu in January. In supply-constrained markets such as New England prices can be much higher than Henry Hub or the national average.
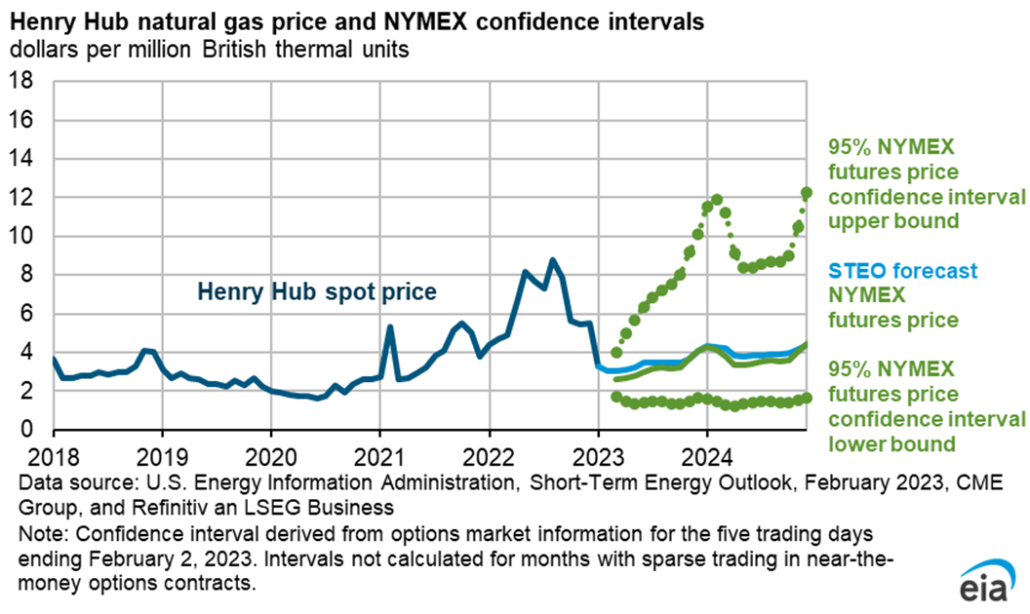
Due to this volatility, there is extreme variation in the range of future potential natural gas prices. The New York Mercantile Price Exchange (NYMEX), forecasts with 95% confidence that natural gas prices will be somewhere between around $1.50/MMBtu and nearly $12/MMBtu by the end of 2023.
In U.S. wholesale power markets, natural gas generation plays a primary role in setting wholesale power prices. This means that higher gas prices cause increases in retail electricity rates, but also create more favorable economics for other generation sources including wind and solar. Regardless of its anticipation of lower gas prices, EIA still expects the portion of gas-fired generation to remain flat at 39% in 2023, while increased solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear power displace coal-fired generation during the year.
EIA also expects liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports to increase 11% in 2023 to 11.8 billion cubic feet. In recent years the United States has become the world’s largest exporter of LNG.
Source: February 2023 Short-Term Energy Outlook (EIA)
in 2023